许多人都知道喝酒太多对肝不好,甚至能引发肝癌等疾病,所以不少人以为少喝酒就能避免肝损伤了,但是英国最新的研究报告显示,现在广泛使用的草甘膦除草剂(是广谱除草剂,常伴随耐草甘膦转基因作物使用,也可做干燥剂;著名品牌是孟山都公司的产品”农达“)在极低浓度下同样可引发非酒精性脂肪肝病(NAFLD)。
这项报告就是在法国科学家塞拉利尼的两年大鼠喂养试验的基础上,进一步用深度分子分析方法和统计分析方法研究得出的结果。
草甘膦在中国广泛使用,中国作为草甘膦最大的生产国,然而国家安全标准对草甘膦最大残留限量规定却比较宽松,而对进口耐草甘膦转基因大豆至今甚至还没有安全标准。为了我们的健康着想,必须要重视这个问题了。
正文
中文译文
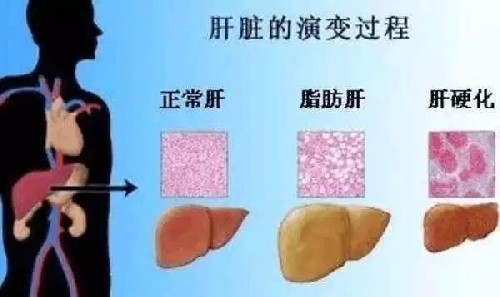
农达在极低浓度下引发非酒精性脂肪肝病
最前沿的分子剖析分析显示常用除草剂农达
在管理机构允许的浓度下造成肝损伤
一个经同行评议的新研究(见文末链接)显示除草剂农达在被全世界管理机构允许的极低浓度下引发非酒精性脂肪肝病。这项研究首次在现实食用环境中实际剂量的农达与某个具体的严重疾病之间,建立起了因果关系。
这项由伦敦国王大学迈克尔·安东尼奥博士领衔的新研究使用了最前沿的剖析方法描述了用极低浓度农达除草剂(基于化学试剂草甘膦)喂养了两年的母鼠肝脏的分子组成。
实验所用的农达中草甘膦的剂量比全世界管理机构允许的浓度低成千上万倍。
该研究发现这些动物遭受了非酒精性脂肪肝病(NAFLD)。
安东尼奥博士说:“我们的研究结果令人担忧,因为它们首次证明在长期食用环境实际剂量的农达与某个具体严重疾病(即非酒精性脂肪肝病)之间,存在因果关系。
“我们的结果还说明管理机构应该重新考虑草甘膦除草剂的安全评估。”
对人类健康潜在而严肃的启示
新的结果证明长期食用低剂量农达---相当于每天每公斤体重草甘膦摄入水平为4纳克---引发了NAFLD,而这个剂量低于欧盟允许剂量七万五千倍,低于美国允许剂量四十三万七千五百倍。
(小编插播:大家猜猜,中国允许的草甘膦残留剂量是多少?1公斤稻谷是纳克,而1公斤小麦粉竟然高达纳克。按一个60公斤的人计算,每日吃0.48克这样的面粉就已经达到实验中的摄入水平了![1])
全世界管理机构都接受用大鼠进行毒性研究来作为人类健康风险的指标,因此这项最新研究的结果对人类健康有着严肃的启示意义。
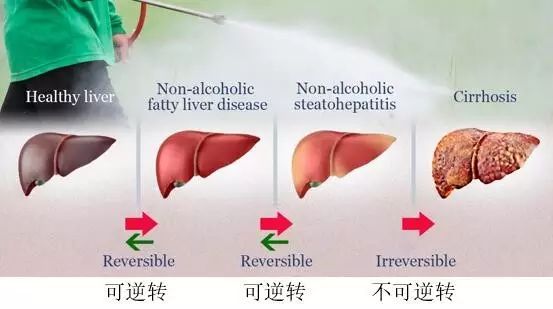
目前NAFLD影响了25%的美国人口[2]以及类似数量的欧洲人口[3]。造成NAFLD的风险因素包括过重或肥胖,有糖尿病,血液中含有高胆固醇或甘油三酸酯(人体脂肪的一个组成部分)。但是,某些人即使不具有任何这类已知风险因素,也出现了NAFLD。
这项新研究提出了这样一个问题:接触农达,是否是迄今为止依然未被意识到的一个风险因素。
NAFLD的症状包括疲劳、虚弱、体重减轻、没有胃口、恶心、腹痛、蜘蛛状血管、皮肤和眼睛(黄疸)发黄、瘙痒、体液积聚、腿和腹部肿胀、心智混乱。
NAFLD会进一步发展至更严重的状况---非酒精性脂肪肝炎(NASH)。NASH导致肝肿胀并受损。
大多数得了NASH的人年龄在40到60岁之间[4],女性比男性更常见。NASH是美国成人肝硬化的主要原因之一。多至25%的NASH成人会有肝硬化。
研究背景
本分析所用大鼠身体组织来自先前法国卡昂大学塞拉利尼教授领衔的研究[5](译注:指的就是著名的塞拉利尼的转基因玉米NK603大鼠两年期喂养试验,当时为检测草甘膦的影响,让一些试验鼠食用了含农达的饮用水)。、
在原先的这个实验中,通过饮用水让大鼠在两年时间内摄入极低的、与环境实际剂量相关的商用农达配方(含0.1ppb农达,相当于50ppt草甘膦)。每天草甘膦摄入量是4纳克/公斤体重,这比管理机构允许的剂量低成千上万倍。
在塞拉利尼教授原先的研究中,经过对器官和血液/尿液的生化水平的分析,发现食用农达的动物比只喝普通饮用水的对照组表现出更大的肝肾损伤发生率。
安东尼奥的团队则对此极低剂量农达实验组的大鼠的身体组织作了独特的跟踪调查,使用了适合于这类研究的深度分子分析方法和统计分析方法。
在第一个跟踪调查[6]中,对母鼠的肝肾作了转录物组学(基因功能图谱)分析。所得结果强烈支持塞拉利尼研究中在解剖学(器官)和血液/尿液生化水平上所观察到的现象,即食用农达的动物比对照组遭受更大的结构和功能损伤。
转录物组学结果显示在喂食农达的动物中纤维化(瘢痕)、坏疽(组织死亡区域)、磷脂质病(干扰脂肪代谢)和线粒体(细胞中的呼吸中心)受损等的发生率更高。
但是,虽然转录物组学分析可以预测一个器官的健康或疾病状态,它并不能提供确定无疑的伤害证据。这主要是因为它不直接测量所研究器官的实际生化性质,并且检测到的基因功能的改变并不总是导致生理组成发生变化并引发疾病。
低剂量农达导致
肝功能失常的确凿证据
在这个新的研究中,研究者对同样的肝脏样本进行了一个蛋白质组成图谱(“蛋白质组学”)和小分子代谢物生化图谱(“代谢物组学”)的跟踪研究,进一步确定了由转录物组学基因表达图谱分析所预示的疾病。
因为蛋白质组学和代谢物组学直接测定器官的实际组成,这些分析方法对其健康或疾病状态给出了确定无疑的评估。
总体上,代谢物组学和蛋白质组学所揭示的紊乱现象,与NAFLD以及进一步发展为脂肪肝炎(严重脂肪肝病)的生化标志特征有大量重合,因此它们确定无疑的证明了长期接触低剂量农达造成了严重肝病。
结果细节
蛋白质组学剖析显示蛋白质受到极大扰乱(占所检测的1906种蛋白中的214个),这反映出由活性氧造成的某种类型的细胞损伤(过氧化物酶体增殖),脂肪变性(严重脂肪肝病)和坏疽(组织死亡区域)。
代谢物组学分析(检测了673种代谢物,55种发生变化)确认了脂肪毒性(过多的脂肪组织)状态和氧化应激。代谢物变化也与严重肝毒性的特征相关。
关于这项新研究
论文基本信息及链接: R, G, Sé GE, Ward M, MN. non- fatty liver in rats to an ultra-low dose of . , 2016; 6:39328.
塞拉利尼和安东尼奥等。多重组学分析显示长期食用极低剂量农达除草剂的大鼠出现非酒精性脂肪肝疾病。《科学报告》,2016;6:39328。
相关链接:
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
英文原文
non- fatty liver
at very low doses
-edge that the liver at doses by .:
The non- fatty liver at very low doses by , a new peer- study shows. The study is the first ever to show a link of at a real-world dose and a .
The new peer- study, led by Dr at King's , used -edge to the of the of rats fed an low dose of , which is based on the , over a 2-year .
The dose of from the was of times below what is by .
The study that these from non- fatty liver (NAFLD).
Dr said: “The of our study are very as they for the first time a link an level of over the long-term and a – non- fatty liver .
“Our also that the of -based .”
for human
The new that long-term of an ultra-low dose of at a daily level of only 4 per of per day, which is 75,000 times below EU and 437,500 below US , in NAFLD.
in rats as of human risks. So the of this study have for human .
NAFLD 25% of the US and of . Risk being or obese, , or high or high (a of body fat) in the blood. , some NAFLD even if they do not have any of these known risk . The new study the of to is a risk .
of NAFLD , , loss, loss of , , pain, -like blood , of the skin and eyes (), , fluid build-up and of the legs and , and .
NAFLD can to the more , non- (NASH). NASH the liver to swell and .
Most with NASH are the ages of 40 and 60 years. It is more in women than in men. NASH is one of the of in in the . Up to 25% of with NASH may have .
to the study
The rat body used in this were from a study led by Prof -Eric Sé of the of Caen, . In this , rats were given an low, dose of a at 0.1ppb (parts per )/50ppt (parts per ) * via water for 2 years. Daily of from the was 4 per of body per day, which is of times below what is by .
of the and blood/urine in the study by Prof Sé a of liver and in the given to given plain water.
Dr ’s group has on the rat body from this ultra-low-dose group, using in-depth and that are for this type of .
In the first , a (gene ) was on the and from the . The the made at an (organ) and blood/urine level in the Sé study – that the of the given more and than the .
The an of (), (areas of dead ), ( fat ) and to (the of in cells) in the -fed .
, is able to or of an organ, it does not proof of harm. This is it does not give a of the of the organ under study. Also, in gene from a test do not in the types of in that could lead to .
of liver from low dose of
In the new study the a (“”) and small (“”) of the same liver to the of by the gene . As the and the of the organ, these a of its or .
, and a with of NAFLD and its to ( fatty liver ). they that liver has from ultra-low dose .
The in
(214 out of 1906 ), as shown by the , a type of cell from ( ), ( fatty liver ) and (areas of dead ).
The (55 out of 673 ) ( fatty ) and . were also with of liver .
The new study
R, G, Sé GE, Ward M, MN. non- fatty liver in rats to an ultra-low dose of . , 2016; 6:39328.
* A 0.1 ppb of the was used, which gave a 50ppt (0.05ppb) of . That is, the was to 0.1 ppb and, given the of in the , this in a of 50 ppt (0.05 ppb) in this .